ASTARTE - ASTARTET - ASHERAH - ISHTAR
She went by many names in different cultures: Zoroastrian, Syrian, Sumerian, and Babylonian in the order of the title. These were Mother Goddesses, rulers of Waters, Stars, and the Fates. They were the principal females of creation.
Astarte means "she of the womb" in Canaanite and Hebrew. When the Hebrews turned from goddess-worship to a religion centered on the male Yahweh (or Jehovah), her name Athtarath was deliberately mis-rendered as Ashtoreth ("shameful thing") and confused with Asherah (see Monaghan). Depicted variously as a death-dealing virgin warrior, a life-giving mother, and a wanton of unbridled sexuality, her emblems were the moon and the morning and evening stars (the planet Venus). Astarte was a warrior goddess of Canaan and Syria who is a Western Semitic counterpart of the Akkadian Ishtar worshipped in Mesopotamia.
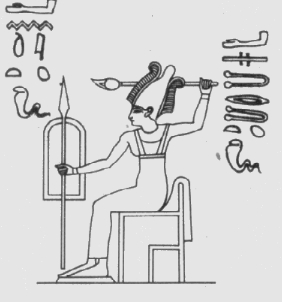
In the Egyptian pantheon to which she was officially admitted during the 18th Dynasty, her prime association is with horses and chariots. On the stela set up near the sphinx by Amenhotep II celebrating his prowess, Astarte is described as delighting in the impressive equestrian skill of the monarch when he was still only crown prince. In her iconography her aggression can be seen in the bull horns she sometimes wears as a symbol of domination. Similarly, in her Levantine homelands, Astarte is a battlefield goddess. For example, when the Peleset (Philistines) killed Saul and his three sons on Mount Gilboa, they deposited the enemy armor as spoils in the temple of "Ashtoreth".
Like Anat, she is the daughter of Re and the wife of the god Seth, but also has a relationship with the god of the sea.
From the fragmentary papyrus giving the legend of Astarte and the sea we learn that Yamm, the sea god, demanded tribute from the gods, particularly Renenutet. Her place is then taken by Astarte called, in this aspect, "daughter of Ptah". The story is lost from that point on but one assumes this liaison resulted in the goddess tempering the arrogance of Yamm.
It should also be noted that outside of Egypt, as well as being a warlike goddess, Astarte seems to have had sexual and motherhood attributes and is sometimes identified with Isis.

Asherah, Athirat ("Lady Asherah of the Sea", "she who gives birth", "wet-nurse of the gods") (Canaanite and Hebrew). Her name seems to come from a root meaning "straight," perhaps signifying both moral rectitude and the upright trees or pieces of wood in which her essence was believed to dwell. In homes, she was represented by a simple, woman-shaped clay figurine with, instead of legs, a tapered base which was inserted in the floor of the home.
She was also depicted as a naked, curly-haired goddess standing on her sacred lion and holding lilies and serpents in upraised hands. According to one source, she was "the force of life, experienced as benevolent and enduring, found in flocks of cattle and groves of trees, evoked in childbirth and in planting time."
She was also called Elat ("Goddess"). Her dying-god consort may have been Yahweh (see Patai). After the shift among the Hebrews to the worship of the male Yahweh, a centuries-long campaign to stamp out her worship began, in which she was deliberately confused with the more wantonly sexual Astarte.

Ishtar
Ishtar ("light-giving queen of heaven") (Babylonian) -
Ishtar, also known as Htar (or Inanna in Sumerian mythology), the name of the chief goddess of Babylonia and Assyria, the counterpart of the Phoenician Astarte. The meaning of the name is not known, though it is possible that the underlying stem is the same as that of Assur, which would thus make her the "leading one" or "chief." At all events it is now generally recognized that the name is Semitic in its origin. Where the name originated is likewise uncertain, but the indications point to Erech where we find the worship of a great mother goddess independent of any association with a male counterpart flourishing in the oldest period of Babylonian history. She appears under various names, among which are Nana, Innanna, Nina and Anunit.
Like Inanna, she loved a dying and reborn vegetation god (Tammuz), whom she descended into the underworld in rescue of after his death. There, she supplicates herself before the queen of the Underworld, Erishkegal (no doubt, the death form of herself). Her emblems were the moon and the morning and evening stars (the planet Venus).
As early as the days of Khammurabi we find these various names which represented originally different goddesses, though all manifest as the chief trait the life-giving power united in Ishtar. Even when the older names are employed it is always the great mother-goddess who is meant. Ishtar is the one goddess in the pantheon who retains her independent position despite and throughout all changes that the Babylonian-Assyrian religion undergoes. Even when Ishtar is viewed as the consort of some chief - of Marduk occasionally in the south, of Assur more frequently in the north - the consciousness that she has a personality of her own apart from this association is never lost sight of.